NASA has discovered something truly unexpected: a Saturn-sized planet orbiting a tiny red dwarf star. Even more exciting, the James Webb Space Telescope is now set to study this strange world in detail. The planet, known as TOI-6894b, orbits a small star in the constellation Leo, and its unique features are challenging what scientists thought they knew about planetary formation.
Let’s dive into why this planet is so weird, what it might teach us, and what the powerful James Webb Telescope could uncover next.
Table of Contents
Discovery
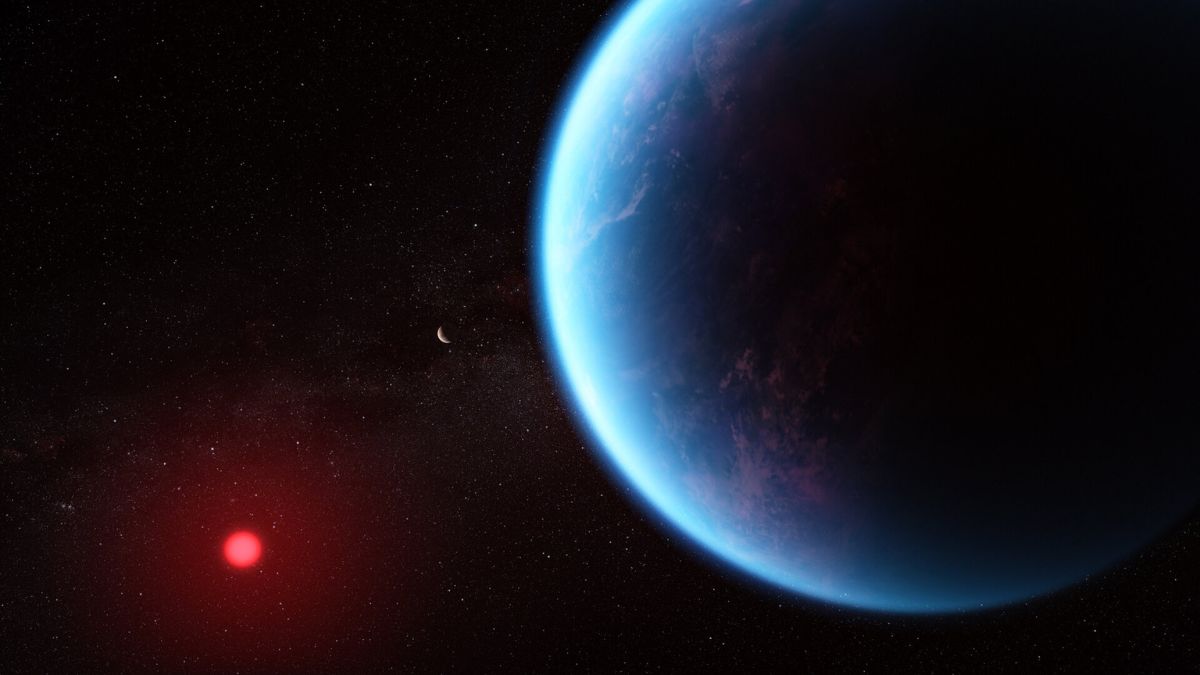
TOI-6894b was discovered using data from NASA’s TESS mission (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite). The planet orbits a red dwarf star—only about 20% the size of our Sun—which makes this finding surprising. That’s because, according to older models, a star this small shouldn’t be able to host such a big planet.
The research was published in Nature Astronomy, and astronomers quickly realized this find was something very special.
Size
This planet is about the same size as Saturn, but it has only half the mass. That means it’s made mostly of gas, but it’s very low in density—astronomers call this kind of planet “fluffy.”
Here’s how it compares:
| Feature | TOI-6894b | Saturn |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | Slightly larger | Reference planet |
| Mass | About half | 1 Saturn mass |
| Density | Very low | Higher than TOI-6894b |
| Host Star | Tiny red dwarf | N/A |
It’s the smallest star ever found with such a large gas planet, which makes this case even more puzzling.
Theories
Normally, planets form through something called core accretion. That’s when small rocks build up into a solid core, then gather gas and dust over millions of years. But that requires lots of raw material—and smaller stars like TOI-6894 don’t usually have enough.
So how did this giant planet form?
Astronomers have two ideas:
- Slow growth without a big gas phase – The planet may have built up slowly but never sucked in huge amounts of gas.
- Disk collapse – The disk of gas around the star may have just collapsed into a planet without forming a rocky core first.
Neither idea fully explains TOI-6894b, but they show how our understanding of planet formation might need to change.
Atmosphere
What makes TOI-6894b even more exciting is its cool atmosphere. At about 420 Kelvin (150°C), it’s much colder than the “hot Jupiters” we usually find. That cooler temperature makes it a better candidate for detecting rare chemical compounds.
Scientists believe this planet may have:
- Methane (CH₄) – Rare in many exoplanet atmospheres
- Ammonia (NH₃) – Never confidently confirmed in any exoplanet atmosphere
Detecting these would be a huge deal for science and could reveal what TOI-6894b’s atmosphere is made of—and how it formed.
Webb
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is now set to take a close look at TOI-6894b. Thanks to its powerful infrared instruments, JWST will analyze the light passing through the planet’s atmosphere to search for chemical signatures.
In the coming months, we might get answers to big questions like:
- Can ammonia actually form in exoplanet atmospheres?
- What chemicals exist on low-density gas giants?
- Could this challenge how we define planet types?
JWST has already revolutionized how we explore deep space, and now it’s turning its eye to TOI-6894b. This mission might reveal secrets not just about one planet—but about how planets like ours could (or couldn’t) form.
Curiosity
The discovery of TOI-6894b proves that space still has plenty of surprises. Just when we think we understand how the universe works, a new object challenges everything. With tools like the James Webb Telescope, the future of space exploration is brighter—and fluffier—than ever.
FAQs
What is TOI-6894b?
A Saturn-sized, low-density gas planet found by NASA.
Why is TOI-6894b important?
It challenges theories on how planets form around small stars.
How was the planet discovered?
Using NASA’s TESS mission and confirmed with telescopes.
What is JWST studying on this planet?
James Webb will analyze its atmosphere for rare compounds.
What’s unique about its atmosphere?
It may contain methane and ammonia, rare in exoplanets.